Wound Healing
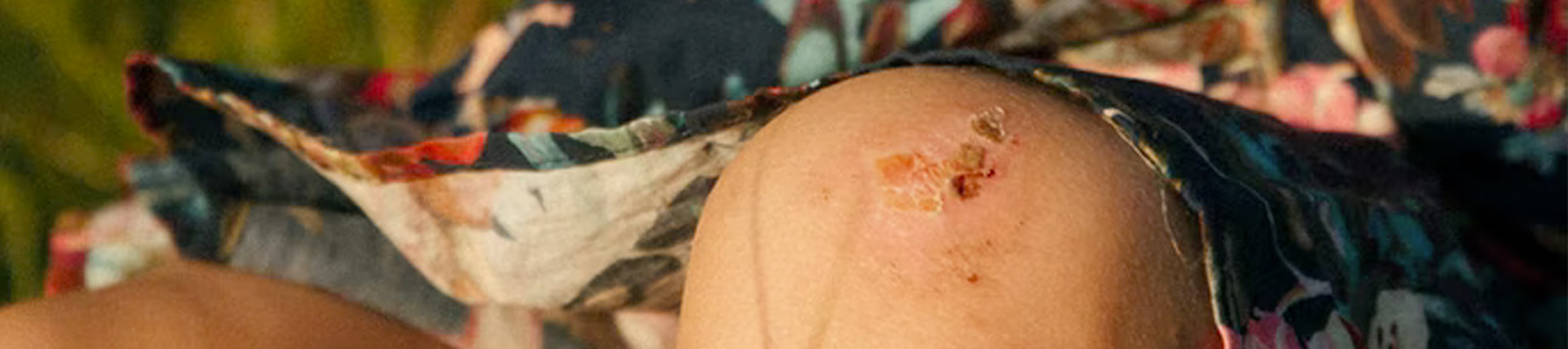
Chronic non-healing wounds affect millions of patients each year and contribute significantly to their morbidity and mortality. These wounds have a substantial impact because of their economic burden and the significant effect on the reduction in quality of life, as well as the increased risk of death for those patients affected by them.

The most common cause of delayed healing in chronic wounds is infection. Microbial contamination of wounds can progress to colonization, to localized infection, through to systemic infection, sepsis, multi-organ dysfunction, and subsequent life- and limb-threatening infection.
The actual determination of infection can be complicated by the presence of biofilms, not on the surface but deep in wound tissue.
Biofilm presence also contributes extensively to keeping the wound in a state of prolonged inflammation by the stimulation of nitric oxide, inflammatory cytokines, and free radicals.









